Retrieving Discarded Conversations From Facebook's Abyss

Retrieving Discarded Conversations From Facebook’s Abyss
Have you ever deleted a Facebook post and then wished you could get it back? Maybe you deleted it accidentally. Or you just wanted to declutter your feed but are now having second thoughts?
If this has happened to you, don’t worry—Facebook has made it easy to recover deleted posts, and we’ll show you how to in this guide.
What Happens When You Delete a Facebook Post?

When you delete a post on Facebook, it doesn’t actually disappear from the platform immediately. Instead, it’s moved to a hidden folder called Trash. Facebook keeps posts in Trash for 30 days before permanently deleting them.
This means that if you accidentally delete a post or change your mind about deleting it later, you have up to 30 days to recover it. However, once the 30 days are up, the post will be gone for good and you won’t be able to recover it.
How to Recover Deleted Facebook Posts From Your Trash Folder
You can recover posts from the trash folder using any device of your choice.
How to Retrieve Deleted Facebook Posts on the App
If you’re using the Facebook app, follow these steps:

Close
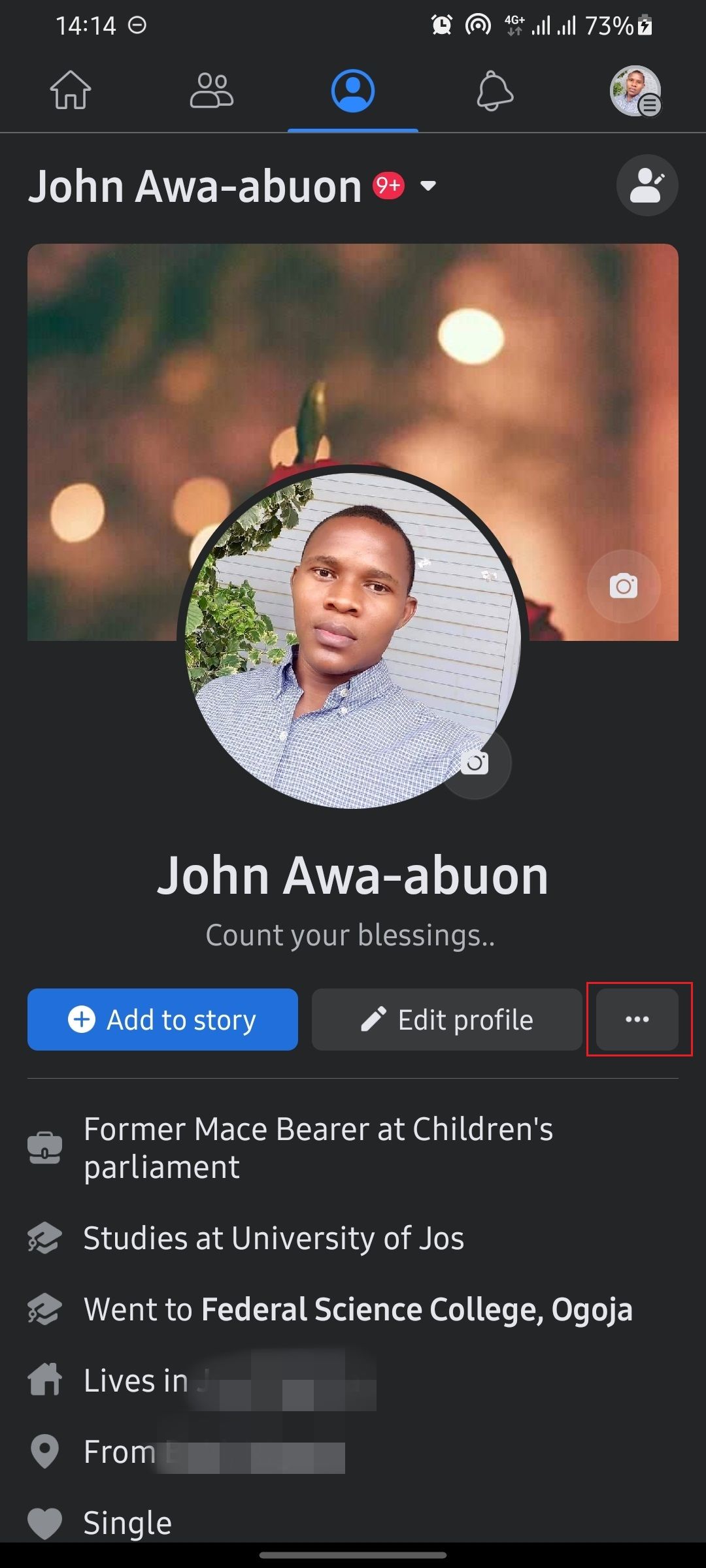
- Launch the Facebook app on your smartphone.
- Navigate to your profile.
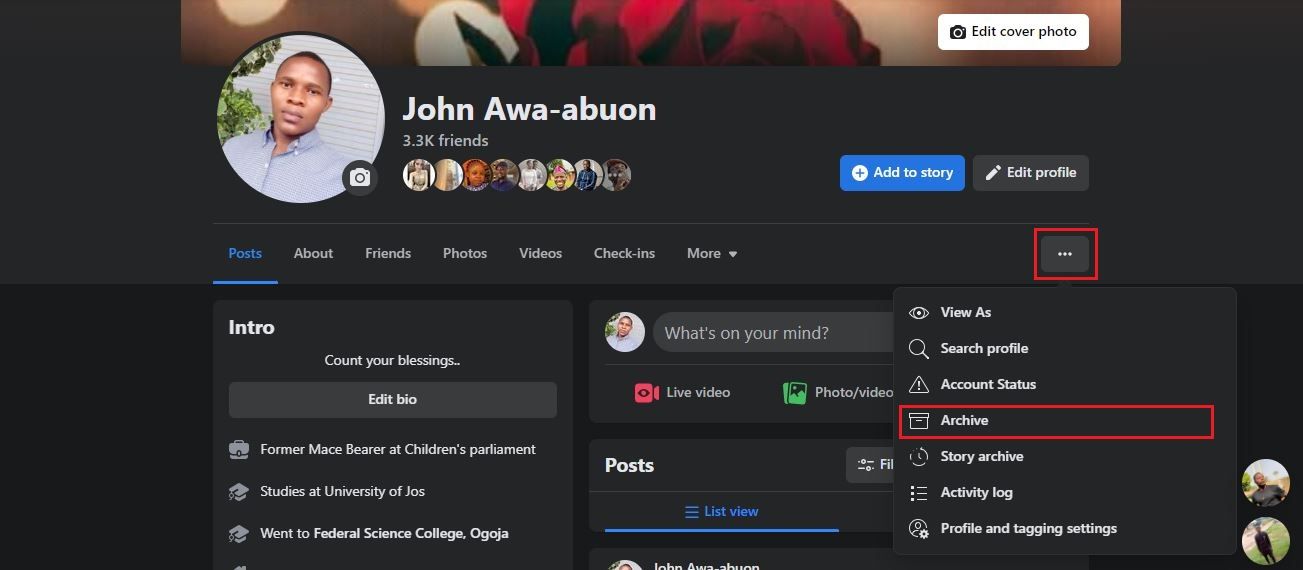
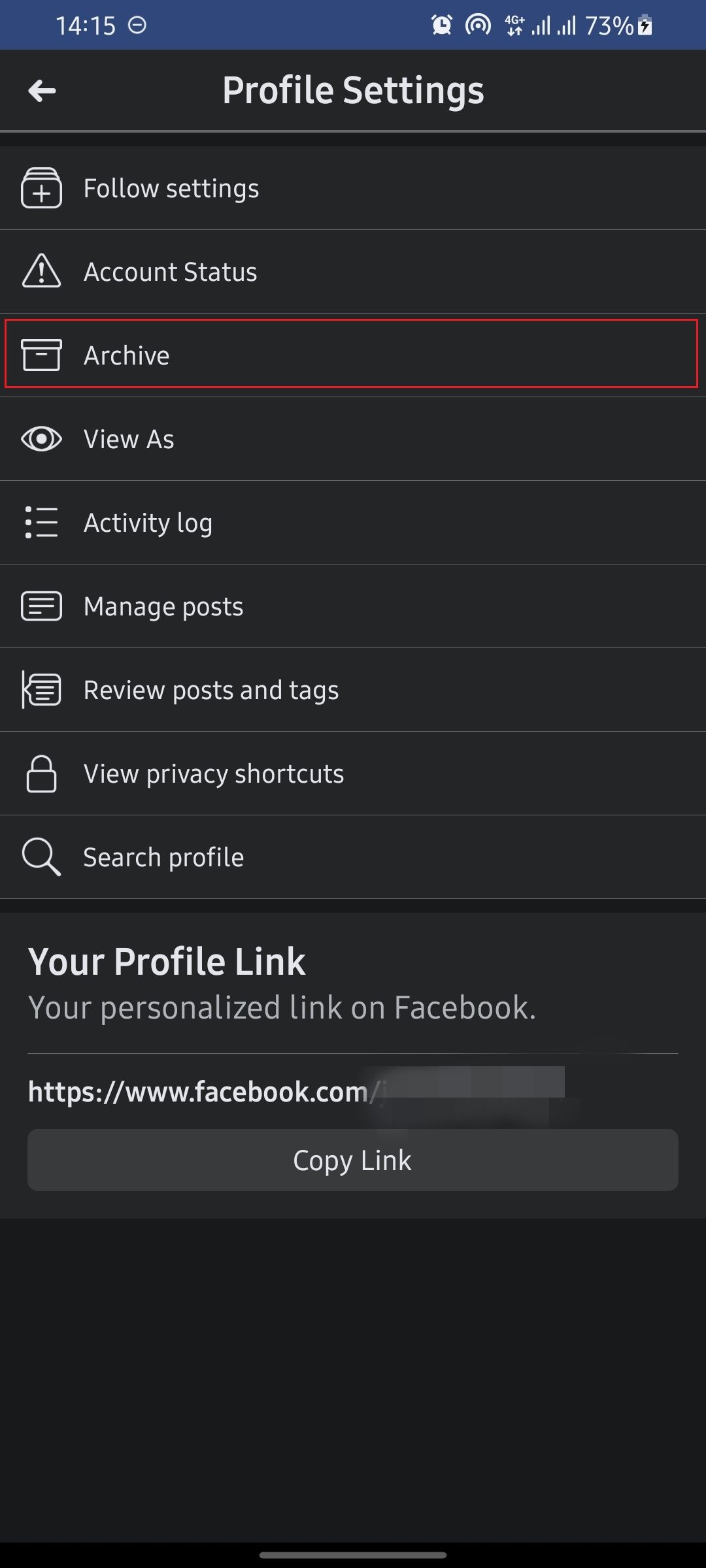
- Tap theellipsis icon (three dots) to reveal profile settings.
- SelectArchive .
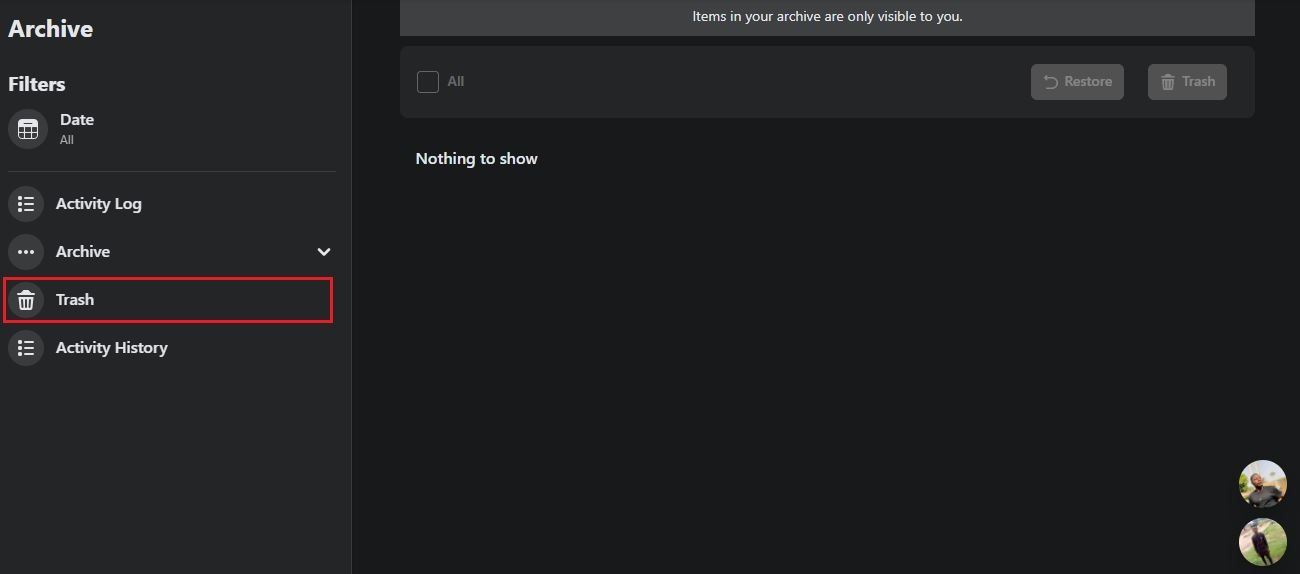
- TapTrash on the Archive page.
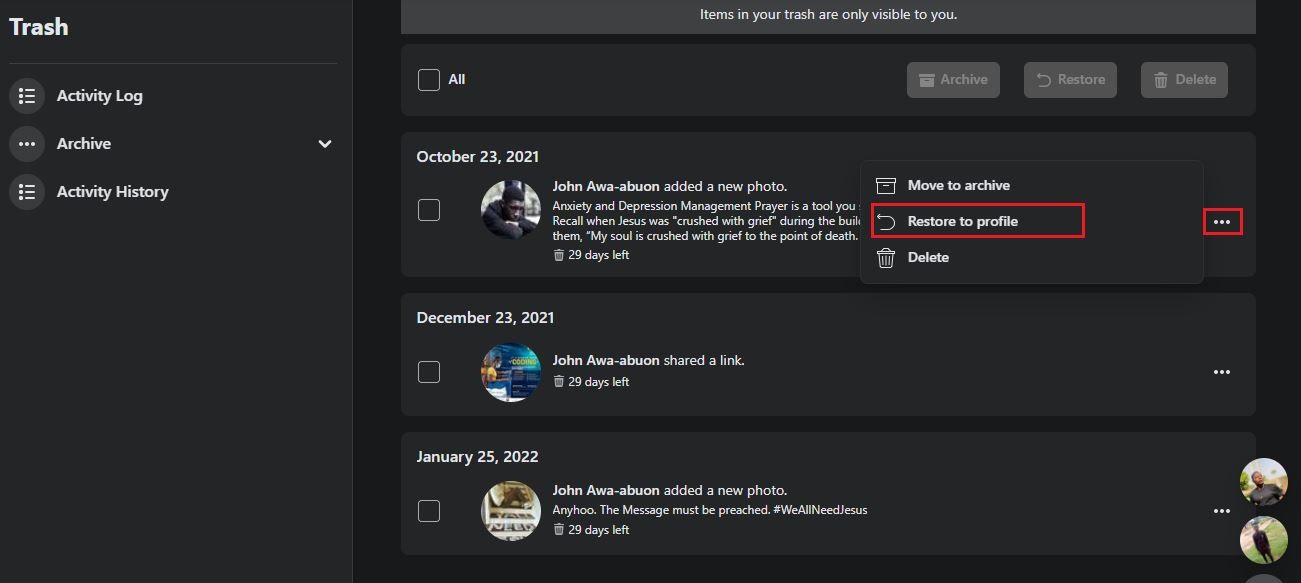
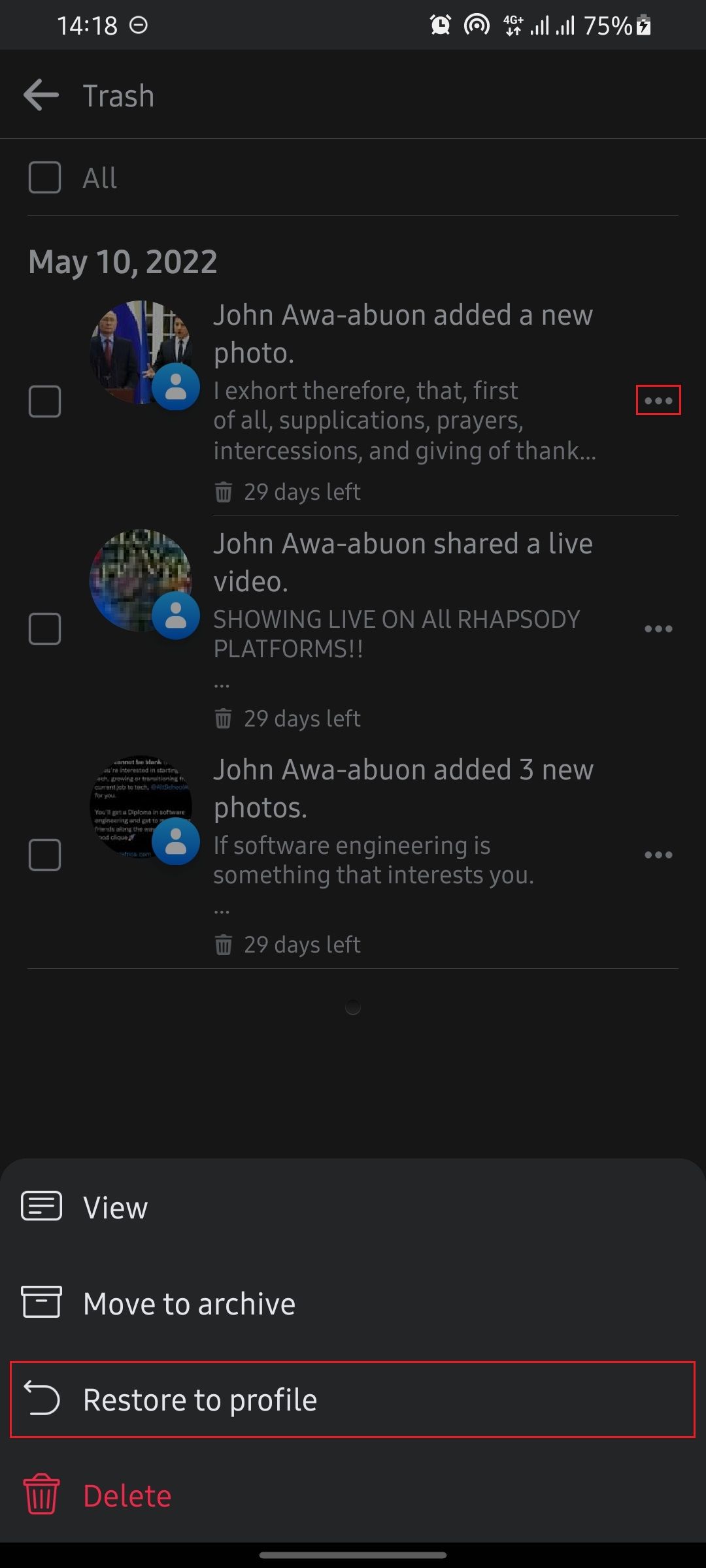
- Find the post you want to recover, then tap theellipsis beside it.
- SelectRestore to profile .
This will restore the post for you.
How to Recover Deleted Posts on the Facebook Website
The process for recovering deleted posts on the Facebook website is similar to that of the Android app, although the icon placement may differ a little.
- Launch a web browser and go to Facebook.com.
- Go to your profile.
- Click on theellipsis icon and selectArchive .
- Click onTrash on the left sidebar.
- Find the post you want to recover, click on theellipsis beside it, then selectRestore to profile .
The Difference Between Deleting and Archiving a Facebook Post
It’s important to note that there is a difference between deleting and archiving a Facebook post. Deleting a Facebook post moves it from your profile page to your trash folder, where it stays for 30 days before it’s permanently deleted.
Archiving a Facebook post means that it’s hidden from your profile page and sent to your archive folder, where it stays indefinitely until you unarchive it or delete it. Our article on how to archive Facebook posts covers how the archive feature works in detail.
Can’t Find Your Post in the Trash Folder?
Turns out that not every deleted post ends up in the Trash folder. If you delete an individual photo, it deletes permanently without entering the Trash folder. Why this is the case is unclear.
Say, for example, you posted a group of seven photos on your profile, and you delete the fourth photo in that group. That fourth photo will disappear permanently without entering the Trash folder. However, if you were to delete the entire post containing all seven photos, then the post would enter the Trash folder.
Another common reason why you may not be able to find a post in the Trash folder is because it has been there for longer than 30 days. Facebook permanently deletes posts from the Trash folder after 30 days, so if you’re looking for a post that was deleted over a month ago, it won’t be there.
Should You Delete or Archive Facebook Posts?
The answer to this question depends on why you’re deleting the post in the first place. If you’re just trying to declutter your feed, then archiving might be the best option. But if you’re trying to get rid of a post permanently, then deleting it is better.
If you’re unsure whether you want to delete or archive a post, consider archiving it. That way, you can always get it back if you change your mind.
- Title: Retrieving Discarded Conversations From Facebook's Abyss
- Author: Michael
- Created at : 2024-07-12 09:58:53
- Updated at : 2024-07-13 09:58:53
- Link: https://facebook.techidaily.com/retrieving-discarded-conversations-from-facebooks-abyss/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.